| June 7, 2013 |
Field Crops 28.421 - 111 |
|
|
How Late Can I Plant Corn?
Joe Lauer, Corn Agronomist
The last USDA-NASS report indicated that 74% of the Wisconsin corn acres have been planted, so we still have over 1 million acres to plant. As weather delays continue, I am getting more questions about, "How late can corn be planted?" The short answer is August 1. However, your production objectives need to change. Most producers will not likely get into the field until next week, so the only locations that can realistically produce grain yet are the southern tier of Wisconsin counties.
Options are rapidly running out.
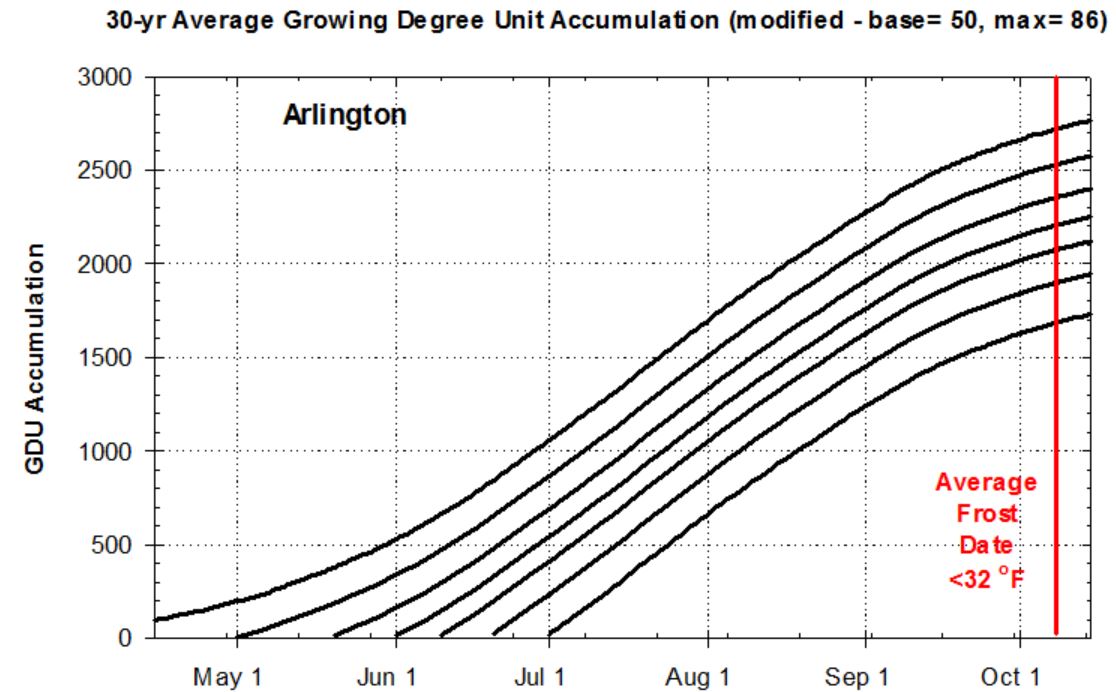
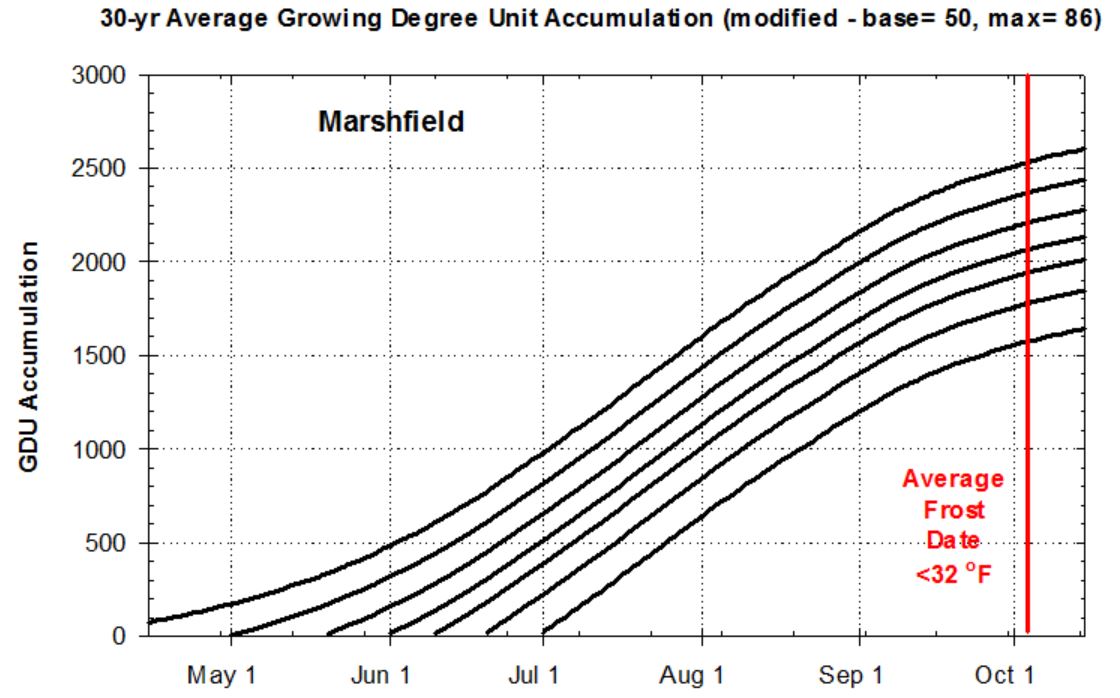
In order to determine what options are still available, you need to know how many Growing Degree Units (GDUs: base=50, max= 86) can still accumulate during the growing season. By back calculating the number of GDUs remaining after a planting date until the average frost date (<32 F), a farmer can determine the best relative maturity for the remaining growing season.The total GDU accumulation between January 1 until the average fall frost date is 2700 GDUs at Arlington and 2500 at
Marshfield (Figure 1). Another 200-300 GDUs are required to dry the crop while standing in the field after it matures. So far, we have accumulated 350 to 400 GDUs at these sites.
Figure 1. Average Growing Degree Unit (GDU) accumulation at Marshfield and Arlington, WI. Weather data obtained from Bill Bland (AWON and UW-Soils) and the Midwest Region Climatological Center. The curves represent 30-yr averages (1983-2012) and begin on January 1, May 1, May 20, June 1, June 10, June 20 and July 1. The average frost date during this 30-yr period was October 3 at Marshfield and October 6 at Arlington.
All hybrids require a similar amount of GDUs to complete grain-filling (~1000 to 1200 GDUs). The main difference between hybrids with different maturity ratings is the time required to achieve silking (Table 1). Long-season hybrids (110-115 d RM) in Wisconsin require about 1500-1700 GDUs, while shorter season hybrids (80-85 d RM) require about 800-900 GDUs. Plants respond to these GDU requirement differences by producing fewer leaves which can be further influenced by photoperiod (latitude).
Table 1. Corn Growing Degree Units (GDUs) required to achieve silking, 50% kernel milk, and maturity growth stages.
Relative
maturity
(days)
|
GDUs to
Silking
|
GDUs to
50% Kernel
Milk
|
GDUs to
Maturity
|
| 110-115
|
1500-1700
|
2450-2650
|
2700-2900
|
| 105-110
|
1350-1500
|
2250-2450
|
2500-2700
|
| 100-105
|
1250-1350
|
2150-2250
|
2400-2500
|
| 95-100
|
1150-1250
|
2050-2150
|
2300-2400
|
| 90-95
|
1000-1150
|
1950-2050
|
2200-2300
|
| 85-90
|
900-1000
|
1800-1950
|
2000-2200
|
| 80-85
|
800-900
|
1500-1800
|
1700-2000
|
Grain and Silage
Table 2 presents suggested hybrid maturities for planting dates during the month of June and the remaining GDUs that can be accumulated by the average frost date. For example, on a June 10 planting date at Arlington there are 2060 GDUs remaining for the growing season (Figure 1). An 80-90 d RM hybrid requires about 1700-2200 GDUs to mature while a 95-100 d RM hybrid would be at 50% Kernel milk after the same number of GDUs (Table 1). Thus, proper maturity selection depends upon the production objective in June.
Table 2 Remaining GDUs and suggested corn hybrid maturity for planting dates at Arlington and Marshfield.
| |
Arlington
|
|
Marshfield |
| Planting date
|
Remaining GDUs
to Frost
|
Hybrid maturity for Grain |
Hybrid maturity for Silage |
|
Remaining GDUs
to Frost
|
Hybrid maturity for Grain
|
Hybrid maturity for Silage
|
| May 1
|
2510
|
105-110
|
105-110
|
|
2360
|
95-100
|
95-100
|
| May 20
|
2340
|
95-100
|
105-110
|
|
2200
|
90-95
|
95-100
|
| June 1
|
2190
|
90-95
|
100-105
|
|
2060
|
80-90
|
90-95
|
| June 10
|
2060
|
80-90
|
95-100
|
|
1935
|
---
|
85-90
|
| June 20
|
1880
|
---
|
90-95
|
|
1770
|
---
|
80-85
|
| July 1
|
1670
|
---
|
80-90
|
|
1570
|
---
|
---
|
Table 2 also describes the last planting dates that can be done for corn to produce grain or silage. The last dates to produce corn grain are June 1 in the north and June 10 in the south. For silage it is June 20 in the north and July 1 in the south. These dates are similar to the last planting dates for soybean (seehttp://soybean.uwex.edu/documents/MGSwitch.pdf)
With corn silage we have two forage quality peaks: one at silking, the other near maturity (see Figure 1 athttp://wisccorn.blogspot.com/2012/07/harvesting-barren-and-poorly-pollinated.html). In a normal silage situation we want to select a maturity that gets us to the second
peak. In a biomass production situation, we want to hit the first peak. To do that at Marshfield on July 1 when we only have 1570 GDUs remaining in the growing season (Table 2), we would chose a hybrid that is 110-115 d RM so that it silks when a frost occurs.
So for silage production situation, long-season hybrids are the ones to choose so that silking occurs when a killing frost occurs. Frost kills the plant and drying will need to occur before it can be properly ensiled. The risk in this situation is that many acres could be ready at the same time and be difficult to harvest in a timely fashion.
Biomass
We have a third option after these last dates for grain and silage. Corn is one of the best options for emergency forage situations where biomass production is the only option left (see http://corn.agronomy.wisc.edu/Management/pdfs/EmergencyForages/2008EmergencyForageCrops.pdf). After August 1, biomass production from corn and other crops like oat are similar. However, corn may still need to be chosen due to herbicide restrictions.
Crop Insurance
Overriding all of these decisions and options is crop insurance. If insured acres not planted by the final planting dates (May 31 for corn for grain), they are considered "late" and a grower has three options:
- Plant late and have a reduced guarantee (a good deal if not too late).
- Plant a different crop, i.e. switch to corn silage or soybeans, or some other forage crop (another good option).
- To trigger Prevented Plant, the grower must satisfy the 20-20 rule: at least 20 acres or 20% of the insured acres must be affected.
- Leave it fallow, collect a "prevented plant indemnity." If the reduced Prevented Plant payment is taken, then the future yield history uses 60% of the approved yield for the Prevented Plant acres, but if a full Prevented Plant is taken, there is no yield history generated for Prevented Plant acres (usually not a good option if a large acreage is involved).
Further Reading
http://www.aae.wisc.edu/pdmitchell/CropInsurance/PP_Options.pdf
http://www.aae.wisc.edu/pdmitchell/CropInsurance/LatePreventPlant2013.pdf