Calculating Grain and Silage Yields for Loan Deficiency Payments
October 14, 1999 6(26):157-158
Joe Lauer, Corn Agronomist
The relationship between corn grain yield and silage yield is important for determining
Loan Deficiency Payments. The current method for calculating this relationship first
appeared in 1972 (Table 1). Much progress has been made in breeding adapted high
yielding hybrids that are more resistant to biotic and abiotic stresses. Does the
old relationship between grain and silage yield still hold?
To describe the relationship between grain and silage yield, data were used where
plots had been split with half of the plot harvested for silage yield and the other
half harvested later for grain yield. Treatments applied to these plots included
various plant density, planting date and row spacing factors. Numerous locations,
hybrids and yield levels were obtained over the 1997 and 1998 growing seasons (n
= 253).
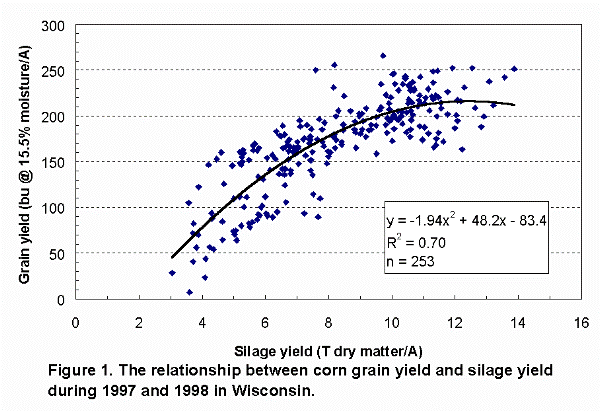
The relationship between grain and silage yield for current hybrids is described
in Figure 1. Grain equivalents at two silage moistures are shown in Table 2. Current
hybrids produce grain yield equivalents greater than that of 1972 levels, by 1.0
to 2.0 bushels of grain per ton of silage at 65% moisture. Using the relationship
developed in 1972 would under estimate grain yields for calculating Loan Deficiency
Payments using modern day hybrids. Further investigation is required to properly
describe this relationship.
|
Table 1. Approximate bushels of dry grain (15.5 percent moisture) contained in a
ton of corn silage (62 to 68 percent moisture).
|
|
Yield of corn grain
|
Bushels of dry grain equivalent/Ton of Silage
|
|
Bu/A
|
Bu/T
|
|
Less than 90
|
5.0
|
|
90-110
|
5.5
|
|
110-130
|
6.0
|
|
130-150
|
6.5
|
|
Over 150
|
7.0
|
|
Derived from "Corn silage for Wisconsin cattle" - A1178 by Jorgensen and
Crowly, 1972
|
|
Table 2. Approximate bushels of grain contained in a ton of corn silage during 1997
and 1998.
|
Grain Yield at
15.5% moisture
|
Silage at 65% moisture
|
|
Silage at 0% moisture
|
Silage
yield
|
Grain equivalent per
Ton of silage
|
|
Silage
yield
|
Grain equivalent per
Ton of silage
|
|
Bu/A
|
T/A
|
Bu/T
|
|
T/A
|
Bu/T
|
|
25
|
7.1
|
3.5
|
|
2.5
|
10.0
|
|
50
|
9.0
|
5.5
|
|
3.2
|
15.8
|
|
75
|
11.1
|
6.8
|
|
3.9
|
19.2
|
|
100
|
13.4
|
7.5
|
|
4.7
|
21.3
|
|
125
|
15.9
|
7.9
|
|
5.6
|
22.4
|
|
150
|
18.7
|
8.0
|
|
6.6
|
22.8
|
|
175
|
22.2
|
7.9
|
|
7.8
|
22.4
|