Corn Insects
Originally written February 1, 2006 | Last updated
March 14, 2016
The foundation of an insect management program includes timely field scouting and
knowing how and when to make insect-control decisions, based on insect numbers or
plant damage, or both.
- Cultural control
- Cultural control
- crop rotation
- tillage operations
- timing of planting and harvesting activities
- Biological control
- Insect resistant crops
- conventional plant breeding
- biotechnology
- Insecticides
- Decision to use an insecticide should be based on:
- information from crop scouting
- understanding of economic thresholds
- knowledge about the potential for the occurrence of insect pests
- Soil-applied insecticides
- Foliar-applied insecticides
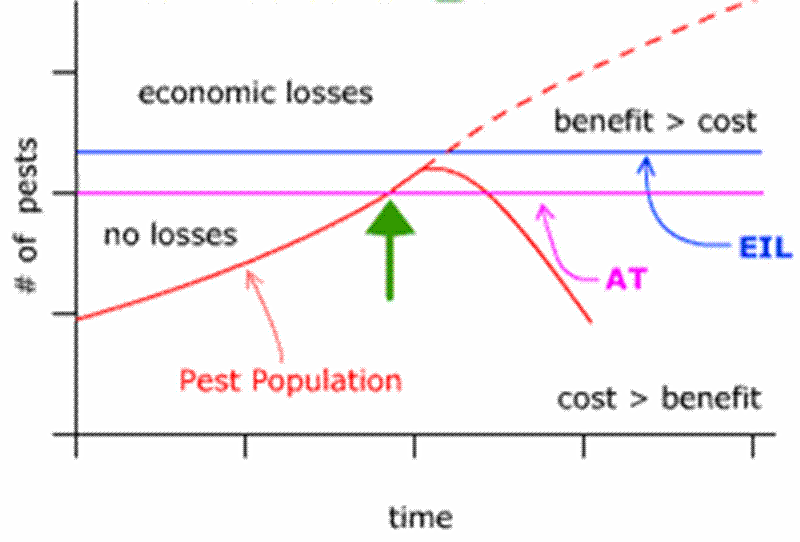
Economic threshold (Action threshold): The pest density or level of damage
at which a control measure is needed to prevent economic loss.
Economic thresholds are not static; they change with fluctuating market values or
control costs
- If the value of corn or soybean increases, the economic threshold declines
- If the cost of control increases, the economic threshold increases.
Economic loss: Occurs when the cost of insect damage in terms of yield or
quality exceeds the cost of control.
|
Insect Groups
- Below ground insects
- Above ground insects
- Stored grain insects
- Occasional insect pests
Gallery of Corn Insects
Clemson University
Often more of a problem than corn diseases in the Midwest
Basic Plan for Scouting Corn in the Corn Belt
- Shortly after crop emergence: early season insects like cutworms, white grubs, wireworms
- mid-June: first generation European corn borer
- July: corn rootworm adults and corn leaf aphids
- late-July and early August: second generation European corn borer
Scouting calendar for corn insects
|
Corn growth
|
Corn stage
|
Insect
|
Calendar
|
Comments
|
|
preemergence
|
seed-VE
|
seedcorn maggot
|
May
|
most common during cool, wet spring or in fields with animal manure or recent green
vegetation
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V3
|
true white grub
|
May
|
most common in areas adjacent to willow and cottonwood trees
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V3
|
wireworm
|
May
|
most common following pasture or CRP grasses
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V3
|
corn flea beetle
|
May
|
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V3
|
hop vine borer
|
May through early June
|
found on lighter soils
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V5
|
black cutworm
|
300 degree days (base 50 F) after significant moth flight; often mid-May to early
June
|
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V5
|
stink bug
|
May
|
uncommon; mostly likely in weedy fields
|
|
emergence and early whorl
|
VE-V5
|
chinch bug
|
May
|
uncommon; mostly following dry summer
|
|
early whorl
|
V1-V6
|
stalk borer
|
late May through June; egg hatch (575-750 degree days base 41 F); begin migration
from grass (1300-1400 degree days base 41 F)
|
most common in fields with grassy weeds or giant ragweed; in clean fields, larvae
will migrate from brome terraces and ditches
|
|
mid-whorl
|
V6-V10
|
corn rootworm larva
|
early to mid-June
|
mostly in continuous corn
|
|
mid-whorl
|
V6-V10
|
armyworm
|
late May to early July
|
most common following no-till sod or in fields with grassy weeds, such as foxtail
|
|
mid- to late-whorl
|
V8-V14
|
European corn borer (first generation)
|
June through early July; begin when corn reaches "knee height" or 200
degree days (basse 50 F) after first moth flight
|
most common in earliest planted fields
|
|
tassel
|
VT
|
corn leaf aphid
|
July through August
|
|
|
tassel to milk stage
|
VT-R3
|
grasshoppers
|
July through early September
|
most common along field margins and grassy areas
|
|
silk
|
R1-R2
|
European corn borer
|
late July through August
|
most common in latest planted fields
|
|
silk
|
R1-R2
|
corn rootworm adult
|
late July through August
|
|
Below ground Insects
Wireworms and Cutworms - are a problem early in the season
Corn rootworms - major problem in Midwest
- Western corn rootworm
- Northern corn rootworm
- Southern corn rootworm (cucumber beetle)
- Damage - root pruning (larvae)
- beetles cause silk damage
- Many corn growers band corn rootworm insecticide at planting (Counter, Furadan,
Lorsban, etc)
Above Ground Insects
European corn borer
- Major Corn Belt problem
- 1st brood - leaf damage
- 2nd brood - Stalk breakage and ear drop
Corn earworm - damages the ear; usually not a major problem
Aphids - corn leaf aphid
Grasshoppers - Common problem in Western US
- More prevalent in western half of Corn Belt
Fall armyworm
Flea beetle
Mites
Stored grain insects
Rice weevil - Most prevalent
Angoumois grain moth
Occasional insect pests
billbugs, chinch bugs, hop vine borer, sod webworm, southern corn leaf beetle, sugarcane
beetle, western bean cutworm, white grubs
Further Reading
To purchase hard copies of these publiThe UWEX Learning Store
Handy Bt Trait Table (written by Chris DiFonzo, Field Crops Entomologist, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI)
Pest Management in Wisconsin
Field Crops .edu/Assets/pdfs/A3646.pdf">Pest Management in Wisconsin
Field Crops UWEX Bulletin A3646
Scouting Corn--A Guide for Wisconsin Corn Production UWEX Bulletin A3547
Insect Resistance Management and Refuge Requirements for Bt
Corn UWEX Bulletin A3857
Seed corn maggot UWEX Bulletin A3820
Corn earworm UWEX Bulletin A3655
Corn Rootworms UWEX Bulletin A3328
Corn Rootworm Pest ID UWEX Bulletin A3631
The European Corn Borer UWEX Bulletin A1220
Western Bean Cutworm: A Pest of Field and Sweet Corn
UWEX Bulletin A3856
Two-spotted Spider Mite Management in Soybean and Corn
UWEX Bulletin A3890
Moth Identification Guide for Blacklight Trap Catch in Wisconsin
UWEX Bulletin A3855
Guidelines for Insecticide Resistance Management (IRM) for
foliar, seed and soil-applied insecticides
Identifying Black Light Trap
Catches
IPM Quickguide: Corn Insect Pests
Wisconsin Integrated Crop Management Manual:
Intro |
Alfalfa |
Corn |
Soybean |
Wheat |
Nutrients |
Weeds |
Complete manual
Pest Management Fast Facts